Small molecules and drugs are often transported within nanocarriers inside the cell, allowing rapid and targeted delivery of drugs. Nanoencapsulation can protect drugs from premature degradation and thus increase its stability in the blood.
The size and type of nanocarriers is critical, as this can determine the efficiency of the drugs and also how they are released in to the blood stream. Nanocapsulation can be performed with different types of nanocarriers which can affect the release and cellular response towards the drugs.
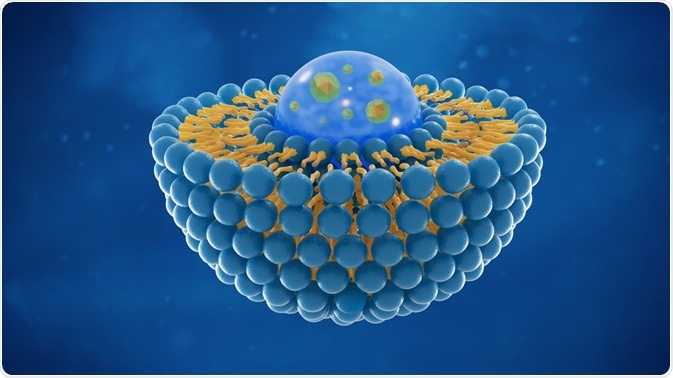
Liposomes
Liposomes have a phospholipid bilayer and are used widely to deliver drugs. Nanoencapsulation in liposomes can prevent the degradation of the drug inside the cells and ensure the delivery of the small molecules at the target site.
The lipids involved in building the liposomes maybe cationic, anionic or neutral based on the nature of use and the drug.
Encapsulation of drugs
For encapsulation of drugs in liposomes, they are directly added to the lipid solution, and the efficiency of encapsulation is measured by the amount of drug which is left in the supernatant, i.e. not encapsulated in the carrier.
The conditions of encapsulation can be changed to increase the efficiency. For example, an anticancer drug is encapsulated in the inner aqueous phase of the liposomes. It is kept for 24 hours at 4°C which leads to more than 90% of the drug being encapsulated.
Surface modifications
The liposomes can interact with the cell surface in a non-specific manner, and this can lead to shorter half-life of the liposomes. They are also rapidly recognized by macrophages and cleared from the blood stream.
This issue can be rectified by coating the liposome with polyethylene glycol (PEG), which leads to a steric barrier and prevents recognition by phagosomes. Aside from PEG, monoclonal antibodies, ligands and peptide sequences can also be added to the liposome surface to improve retention and targeted delivery.
Drug loading and release
Drugs can be loaded by either passive or active methods. In the passive method, a dried lipid film is rehydrated along with the drug molecules, which leads to drug loaded liposomes. In the active method, concentration or pH gradients are used to load drugs on formed liposomes.
The release of drugs from liposomes can be influenced by the addition of functional head groups, lipids and linker groups. The release may be achieved by pH and temperature dependent techniques, or by thiolysis of disulfide bonds in the lipid membrane.
Cellular response
The liposomes with the drug molecules are taken up by endocytosis, and then the drug is released.
Polymeric micelles
Polymeric micelles are also being widely used for drug delivery as they are a small size and have high structural stability. Micelles are created using hydrophobic or electrostatic interactions, or metal ion complexation. The core of micelles is formed by hydrophobic parts of copolymers, and they can influence the stability, loading, and release of the drugs.
Surface modifications
The surface of micelles can be modified by the addition of PEG, ligands, receptors, or antibodies. These modifications increase the circulation time of micelles in the blood stream.
Drug loading and release
The drugs can be loaded onto micelles by physical or chemical methods. The release is influenced by the length of core forming polymer, affinity between the drug and core material, and the quantity of drug loaded.
Cellular Response
The uptake in cells can also be modified using liposomes. For example, micelles where PEG (polyethylene glycol) and PE (phosphatidylethanolamine) are conjugated have been shown to have a 8-fold higher uptake.
Carbon nanotubes
Carbon nanotubes are sheets of graphite which have been rolled into a cylinder. They are nanoscale materials and have high conductivity and strength. They have also been used to deliver drugs and molecules.
Two kinds of nanotubes are used: single-walled, which has single sheet rolled in to a cylindrical tube, and multi-walled nanotubes, where several nanotubes are placed concentrically inside one another.
Surface modifications
Single-walled carbon nanotubes can trigger reactions not only at their ends but also along the tube. This ability can be changed by controlled chemical functionalization.
Multi-walled carbon nanotubes can be modified to improve its interfacial interactions. For example, selectively attaching gold particles to these multi-walled carbon nanotubes enhance the potential applications beyond the pharmaceutical industry.
Drug loading and release
Drugs can be loaded onto carbon nanotubes by one of two methods. The first method is where the drug is incorporated into the carbon nanotubes while is is being made.
In the second method, the drug is loaded onto the carbon nanotubes by adsorption. Varying the pH or temperature then allows the drug to be released from the carbon nanotubes.
Cellular response
Factors such as size and surface modifications influence the cellular response to carbon nanotubes.

